Heterogeneity among individuals in a population is one of the
important factors that influence the rate of population spread. To incorporate
the population heterogeneity into dispersal rate, we assume that the traveling
duration varies following a gamma distribution with a shape parameter k, where
(1/k ) indicates the heterogeneity in the traveling duration. The resultant
distribution of the traveling distance, that is called dispersal function, is
then expressed by using a modified Bessel function of the second kind of order
(k - 1). It is shown that the front of the distribution spreads with time
in an accelerated manner during an early phase of expansion if the heterogeneity
is sufficiently large, which is consistent with the results from previous studies
of biological invasions. By using the data obtained from mark-recapture experiments
using traps, we can obtain the maximum likelihood estimates of three parameters:
heterogeneity in the traveling duration, which is defined by (1/k ); the
mean dispersal ability, which is defined by the product of the diffusion coefficient
and the mean traveling duration; and the trap efficiency. The usefulness of this
model is shown by using the data of mark-recapture experiments with the common
cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). (Copyright
by the Society of Population Ecology and Springer-Verlag Tokyo)
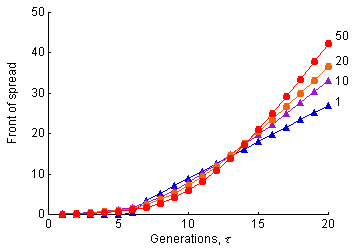
Figure 2. Expansion of the distribution front. The numbers beside curves
indicate the heterogeneity in the traveling duration (1/k) used in the
simulation. n0 = 1, nc = 1, R0 =
2, and m = 1. Accelerated increase occurs in an early stage of expansion.
(Copyright by the Society of Population Ecology and Springer-Verlag Tokyo)